Note: Before you begin, make sure to git pull this repository to bring your local repo up to date with the online one.
We will be working with many of the following packages in this session:
readr: Efficiently import data into R
tibble: The spreadsheet workhose of Tidyverse
dplyr: Data manipulation
tidyr: Tidy your data
ggplot2: A different grammar of graphics
forcats: Simplify factors
purrr: Repetitive tasks
While you can install them one package at a time, you can also install all at once:
We will be working with the following data set for today’s exercise:
Tidyverse package readr has an improved set of functions over their base-R counterparts. These functions are a lot faster, which is advantageous when reading very large data sets. For such large files, readr functions have a progress bar showing the amount of data read in real time. In base-R, you are just waiting for the prompt to return.
read_csv (base-R: read.csv)
read_tsv (base-R: read.table)
read_delim (base-R: read_delim)
read_log (no base-R function)
When you read in a data frame (i.e. a spreadsheet), with any type of column delimiter (comma, tab, space or some other symbol), readr converts it into a format called tibble, which is a modified data frame. A tibble provides many ease of use features as we will see below.
git clone function on github.com/nytimes/covid-19-data to make a local copy.colleges folder.
cd covid-19-data/
ls -lh
-rw-r--r--@ 1 vikram staff 1.3K Feb 24 06:41 LICENSE
-rw-r--r--@ 1 vikram staff 2.7K Feb 24 06:41 NEW-YORK-DEATHS-METHODOLOGY.md
-rw-r--r--@ 1 vikram staff 3.1K Feb 24 06:41 PROBABLE-CASES-NOTE.md
-rw-r--r--@ 1 vikram staff 21K Jun 7 18:28 README.md
drwxr-xr-x@ 4 vikram staff 128B Jun 7 18:28 colleges
drwxr-xr-x@ 4 vikram staff 128B Feb 24 06:41 excess-deaths
drwxr-xr-x@ 5 vikram staff 160B Jun 7 18:28 live
drwxr-xr-x@ 4 vikram staff 128B Feb 24 06:41 mask-use
drwxr-xr-x@ 5 vikram staff 160B Jun 7 18:28 prisons
drwxr-xr-x@ 8 vikram staff 256B Jun 7 18:28 rolling-averages
-rw-r--r--@ 1 vikram staff 3.9M Jun 7 18:28 us-counties-recent.csv
-rw-r--r--@ 1 vikram staff 55M Jun 7 18:28 us-counties.csv
-rw-r--r--@ 1 vikram staff 855K Jun 7 18:28 us-states.csv
-rw-r--r--@ 1 vikram staff 12K Jun 7 18:28 us.csv
cd colleges
ls -lh
-rw-r--r--@ 1 vikram staff 6.6K Jun 7 18:28 README.md
-rw-r--r--@ 1 vikram staff 157K Jun 7 18:28 colleges.csvThe README.md file contains metadata and other details for the information stored inside colleges.csv.
Use the read_csv function to import the data into R. Make sure to use the tidyverse function, which has an _ instead of the base-R ..
library(tidyverse)
college <- read_csv("colleges.csv")
── Column specification ──────────────────
cols(
date = col_date(format = ""),
state = col_character(),
county = col_character(),
city = col_character(),
ipeds_id = col_character(),
college = col_character(),
cases = col_double(),
cases_2021 = col_double(),
notes = col_character()
)You will notice that unlike the base-R function, read_csv tells you how it has interpreted data in each of the columns. There are several types of identifiers here as follows:
col_date
col_character
col_double
These are data type specifications implemented by readr. For example, the column with date header is being correctly identified as date time data. Information in column state is being read correctly as characters, and finally number of cases (cases) is being read as double, which is a type of numerical data.
Let’s now check what our data looks like:
college
# A tibble: 1,948 x 9
date state county city ipeds_id college cases cases_2021 notes
<date> <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <chr>
1 2021-05-26 Alaba… Madison Hunts… 100654 Alabama A&M… 41 NA NA
2 2021-05-26 Alaba… Montgo… Montg… 100724 Alabama Sta… 2 NA NA
3 2021-05-26 Alaba… Limest… Athens 100812 Athens Stat… 45 10 NA
4 2021-05-26 Alaba… Lee Auburn 100858 Auburn Univ… 2742 567 NA
5 2021-05-26 Alaba… Montgo… Montg… 100830 Auburn Univ… 220 80 NA
6 2021-05-26 Alaba… Walker Jasper 102429 Bevill Stat… 4 NA NA
7 2021-05-26 Alaba… Jeffer… Birmi… 100937 Birmingham-… 263 49 NA
8 2021-05-26 Alaba… Limest… Tanner 101514 Calhoun Com… 137 53 NA
9 2021-05-26 Alaba… Tallap… Alexa… 100760 Central Ala… 49 10 NA
10 2021-05-26 Alaba… Coffee Enter… 101143 Enterprise … 76 35 NA
# … with 1,938 more rowsAs you will notice, readr has converted this data frame into a tibble, and it shows some useful information about the file instead of just spitting out all columns and all rows to the screen. Below each column header, a tibble identifies the type of data contained within it (enclosed within <>).
A tibble will always print the first 10 rows of data unless you ask for more. Depending upon the number of columns available in the data, it will also show only as many as it can comfortably fit on screen.
If you are familiar with the pipe function in Unix (|), the R pipe works similarly (albeit it uses a different symbol). The goal is to use output from one command and pass it onto another function. Just like the Unix pipe, the R pipe can also be nested as many times as you want. We will see some examples below.
What if you wanted to print 15 rows of data from the above tibble to the screen?
college %>% print(n=15, width=Inf)
# A tibble: 1,948 x 9
date state county city ipeds_id college cases cases_2021 notes
<date> <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <chr>
1 2021-05-26 Alabama Madison Huntsville 100654 Alabama A&M University 41 NA NA
2 2021-05-26 Alabama Montgomery Montgomery 100724 Alabama State University 2 NA NA
3 2021-05-26 Alabama Limestone Athens 100812 Athens State University 45 10 NA
4 2021-05-26 Alabama Lee Auburn 100858 Auburn University 2742 567 NA
5 2021-05-26 Alabama Montgomery Montgomery 100830 Auburn University at Montgomery 220 80 NA
6 2021-05-26 Alabama Walker Jasper 102429 Bevill State Community College 4 NA NA
7 2021-05-26 Alabama Jefferson Birmingham 100937 Birmingham-Southern College 263 49 NA
8 2021-05-26 Alabama Limestone Tanner 101514 Calhoun Community College 137 53 NA
9 2021-05-26 Alabama Tallapoosa Alexander City 100760 Central Alabama Community College 49 10 NA
10 2021-05-26 Alabama Coffee Enterprise 101143 Enterprise State Community College 76 35 NA
11 2021-05-26 Alabama Etowah Gadsden 101240 Gadsden State Community College 67 5 NA
12 2021-05-26 Alabama Montgomery Montgomery 101435 Huntingdon College 0 NA NA
13 2021-05-26 Alabama Calhoun Jacksonville 101480 Jacksonville State University 229 10 NA
14 2021-05-26 Alabama Covington Andalusia 101602 Lurleen B. Wallace Community College 19 NA NA
15 2021-05-26 Alabama Perry Marion 101648 Marion Military Institute 45 19 NA Inf option for the width of the tibble. Because this tibble is small, it fits comfortable on our screen. However, if your tibble was much wider than this, you could restrict the width to match that of your display. For example, try the following three commands and try to notice the differences between the three outputs:college %>% print(n=15, width=150)
college %>% print(n=15, width=100)
college %>% print(n=15, width=70)What was different about the outputs?
If you wanted to find out how many different institutions have been represented in this data set:
college %>% count(college)
# A tibble: 1,936 x 2
college n
<chr> <int>
1 Abilene Christian University 1
2 Abraham Baldwin Agricultural College 1
3 Academy of Art University 1
4 Adams State University 1
5 Adelphi University 1
6 Adirondack Community College 1
7 Adrian College 1
8 AdventHealth University 1
9 Agnes Scott College 1
10 Air Force Institute of Technology-Graduate School of Engineering & Man… 1
# … with 1,926 more rowsThis shows that there are a total of 1936 institutions covered here. count is a function from the library dplyr, part of core Tidyverse. The pipe (%>%) is not part of tidyverse; it comes from a package named magritter which is a dependency for tidyverse.
college %>% filter(state="Nevada")
# A tibble: 7 x 9
date state county city ipeds_id college cases cases_2021 notes
<date> <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <chr>
1 2021-05-26 Nevada Clark Las Vegas 182005 College of Southern Nevada 440 111 NA
2 2021-05-26 Nevada Elko Elko 182306 Great Basin College 43 9 NA
3 2021-05-26 Nevada Clark Henderson 441900 Nevada State College 48 10 NA
4 2021-05-26 Nevada Washoe Reno 182500 Truckee Meadows Community College 58 10 NA
5 2021-05-26 Nevada Clark Las Vegas 182281 University of Nevada, Las Vegas 719 212 NA
6 2021-05-26 Nevada Washoe Reno 182290 University of Nevada, Reno 1544 335 NA
7 2021-05-26 Nevada Carson City Carson City 182564 Western Nevada College 53 4 NA college %>% filter(state="Hawaii") %>% select(1:3, 7)
# A tibble: 9 x 4
date state county cases
<date> <chr> <chr> <dbl>
1 2021-05-26 Hawaii Honolulu 55
2 2021-05-26 Hawaii Honolulu 1
3 2021-05-26 Hawaii Honolulu 1
4 2021-05-26 Hawaii Honolulu 5
5 2021-05-26 Hawaii Honolulu 4
6 2021-05-26 Hawaii Maui 2
7 2021-05-26 Hawaii Hawaii 10
8 2021-05-26 Hawaii Honolulu 73
9 2021-05-26 Hawaii Honolulu 2col %>% filter(state=="California") %>% select("date", "state", "county", "cases")
# A tibble: 90 x 4
date state county cases
<date> <chr> <chr> <dbl>
1 2021-05-26 California San Francisco 0
2 2021-05-26 California Los Angeles 101
3 2021-05-26 California Los Angeles 108
4 2021-05-26 California Kern 0
5 2021-05-26 California Los Angeles 99
6 2021-05-26 California Riverside 25
7 2021-05-26 California Los Angeles 123
8 2021-05-26 California Ventura 47
9 2021-05-26 California San Luis Obispo 2021
10 2021-05-26 California Los Angeles 61
# … with 80 more rowsCalifornia data consists of 90 rows altogether.
You have just used two new functions from the dplyr package. If you are curious about details of these functions, you can always look at the package help menu:
?filter
Help on topic ‘filter’ was found in the following packages:
Package Library
dplyr /Library/Frameworks/R.framework/Versions/4.0/Resources/library
stats /Library/Frameworks/R.framework/Versions/4.0/Resources/librarycol %>% filter(state=="California") %>% select("date", "state", "county", "cases") %>% ggplot() + geom_point(aes(x=date, y=cases))
setwd("../covid-19-data")
list.files()
[1] "colleges" "excess-deaths" "LICENSE" "live"
[5] "mask-use" "NEW-YORK-DEATHS-METHODOLOGY.md" "prisons" "PROBABLE-CASES-NOTE.md"
[9] "README.md" "rolling-averages" "us-counties-recent.csv" "us-counties.csv"
[13] "us-states.csv" "us.csv" counties <- read_csv("us-counties.csv")
counties
# A tibble: 1,394,421 x 6
date county state fips cases deaths
<date> <chr> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <dbl>
1 2020-01-21 Snohomish Washington 53061 1 0
2 2020-01-22 Snohomish Washington 53061 1 0
3 2020-01-23 Snohomish Washington 53061 1 0
4 2020-01-24 Cook Illinois 17031 1 0
5 2020-01-24 Snohomish Washington 53061 1 0
6 2020-01-25 Orange California 06059 1 0
7 2020-01-25 Cook Illinois 17031 1 0
8 2020-01-25 Snohomish Washington 53061 1 0
9 2020-01-26 Maricopa Arizona 04013 1 0
10 2020-01-26 Los Angeles California 06037 1 0
# … with 1,394,411 more rowscounties %>% filter(state=="California")
# A tibble: 25,907 x 6
date county state fips cases deaths
<date> <chr> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <dbl>
1 2020-01-25 Orange California 06059 1 0
2 2020-01-26 Los Angeles California 06037 1 0
3 2020-01-26 Orange California 06059 1 0
4 2020-01-27 Los Angeles California 06037 1 0
5 2020-01-27 Orange California 06059 1 0
6 2020-01-28 Los Angeles California 06037 1 0
7 2020-01-28 Orange California 06059 1 0
8 2020-01-29 Los Angeles California 06037 1 0
9 2020-01-29 Orange California 06059 1 0
10 2020-01-30 Los Angeles California 06037 1 0
# … with 25,897 more rows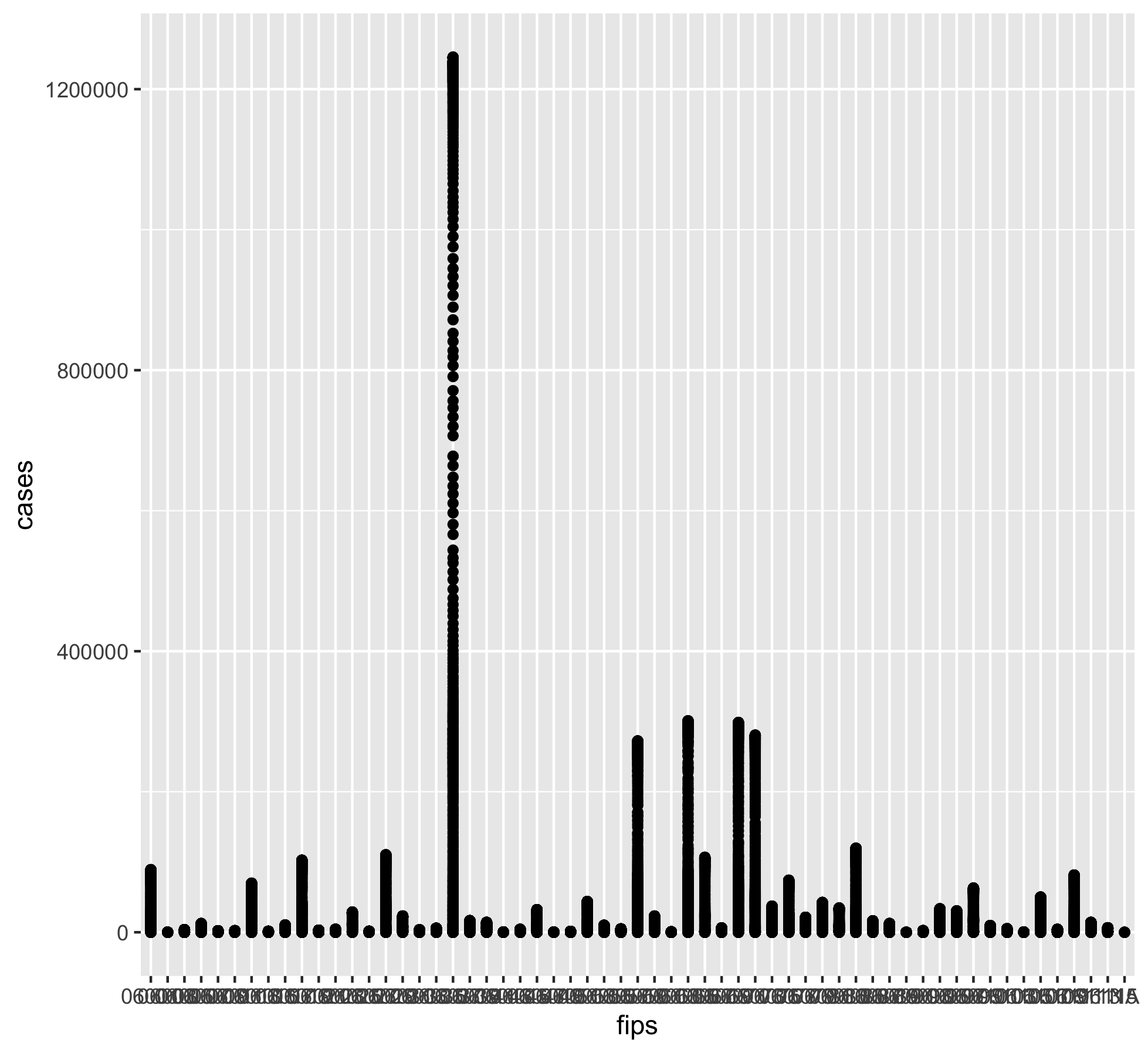
counties %>% filter(state == "California") %>% filter(cases > 1200000)
# A tibble: 94 x 6
date county state fips cases deaths
<date> <chr> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <dbl>
1 2021-03-05 Los Angeles California 06037 1200764 21910
2 2021-03-06 Los Angeles California 06037 1202513 22008
3 2021-03-07 Los Angeles California 06037 1203799 22029
4 2021-03-08 Los Angeles California 06037 1204665 22041
5 2021-03-09 Los Angeles California 06037 1205924 22099
6 2021-03-10 Los Angeles California 06037 1207361 22213
7 2021-03-11 Los Angeles California 06037 1208672 22304
8 2021-03-12 Los Angeles California 06037 1208678 22304
9 2021-03-13 Los Angeles California 06037 1210286 22446
10 2021-03-14 Los Angeles California 06037 1210920 22474
# … with 84 more rows
counties %>% filter(state == "California") %>% filter(deaths > 10000)
# A tibble: 159 x 6
date county state fips cases deaths
<date> <chr> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <dbl>
1 2020-12-30 Los Angeles California 06037 756412 10056
2 2020-12-31 Los Angeles California 06037 770915 10345
3 2021-01-01 Los Angeles California 06037 790895 10552
4 2021-01-02 Los Angeles California 06037 806523 10682
5 2021-01-03 Los Angeles California 06037 818959 10773
6 2021-01-04 Los Angeles California 06037 827843 10850
7 2021-01-05 Los Angeles California 06037 840956 11071
8 2021-01-06 Los Angeles California 06037 852510 11328
9 2021-01-07 Los Angeles California 06037 871749 11545
10 2021-01-08 Los Angeles California 06037 889787 11863
# … with 149 more rowsAccess the prisons/ directory within the NYT covid-19-data repository and import the facilities.csv data into R (store it as an object fac).
How many rows and columns of data is present in the facilities data set?
Use the pipe function to display only these columns: facility name, state, inmate cases, inmate deaths
Count the total number of prison facilities.
Count the number of facilities per state.
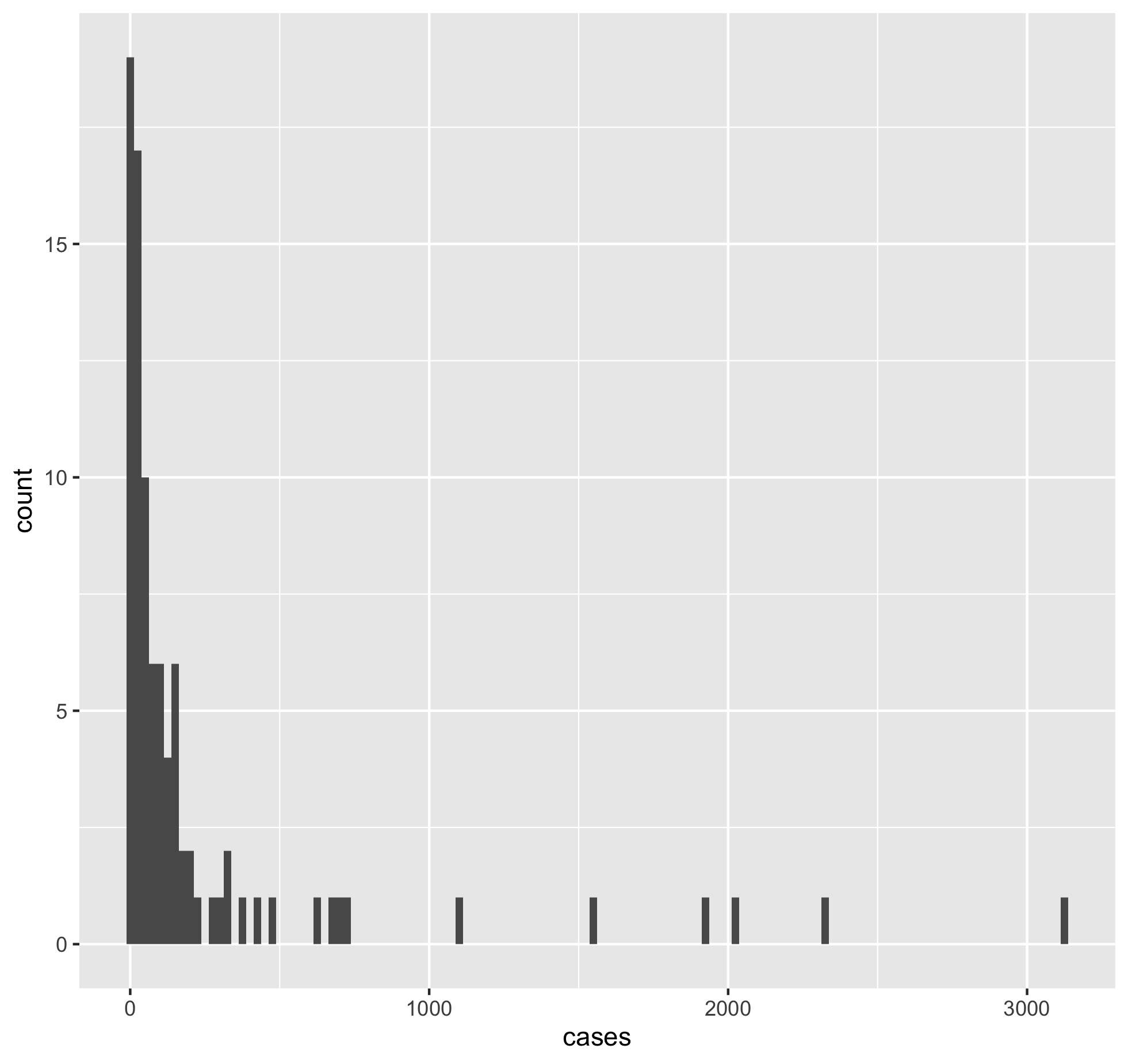
Using the fac_sub tibble make a scatterplot of inmate cases vs inmate deaths in ggplot.
Which state had the highest number of inmate cases or deaths?
First install the following two packages:
maps
mapdata
Load the packages
Create base USA map object
usa <- map_data('usa')
states <- map_data('state')
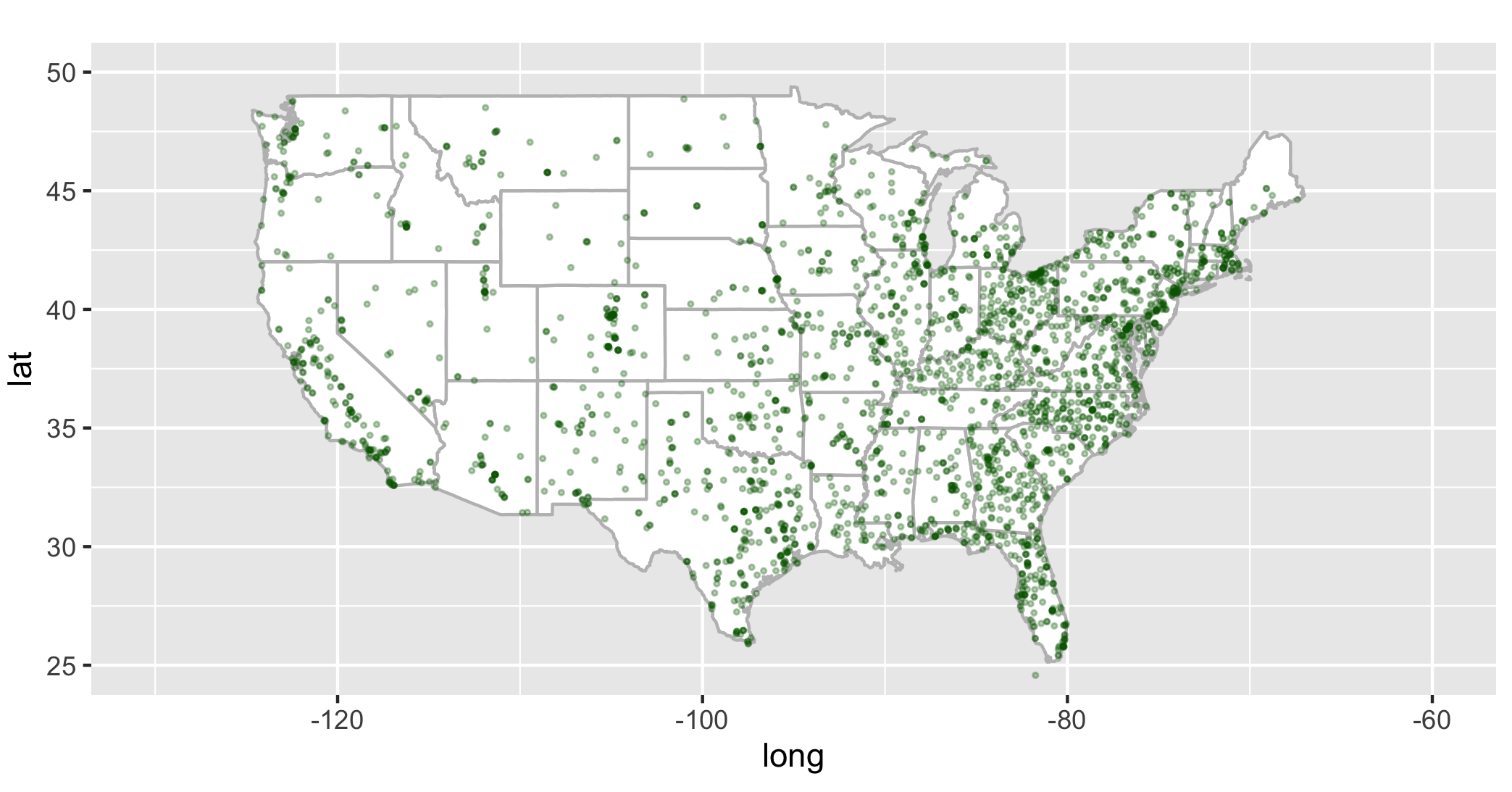
usa_base <- ggplot(data=states) + geom_polygon(aes(x=long, y=lat, fill=I('white'), group=group), color='gray') + coord_fixed(1.3) + guides(fill=FALSE)
usa_base + geom_point(data=fac, aes(x=facility_lng, y=facility_lat), color="darkgreen", cex=0.5, alpha=3/10) + coord_fixed(xlim=c(-130, -60), ylim=c(25,50), ratio=1.3)